 Cytochromes P450 (CYP) is a superfamily of proteins involved in metabolism and inactivation of foreign substances and toxins. Each protein in this family is highly specialized with unique, dedicated pathways inside the cell.
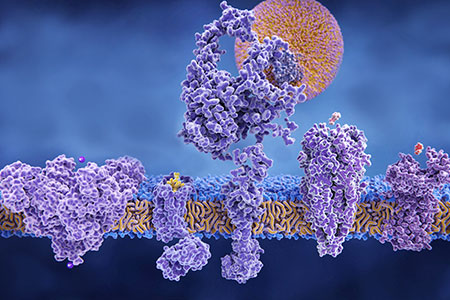
Cytochromes P450 (CYP) is a superfamily of proteins involved in metabolism and inactivation of foreign substances and toxins. Each protein in this family is highly specialized with unique, dedicated pathways inside the cell. CYPs are transmembrane proteins commonly found in the plasma membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum in liver cells and interact with ligands on both sides1. Using heme as a cofactor, these proteins aid in the processing and excretion of drugs and toxins and are essential for maintaining homeostasis. In fact, CYPs oxidize 70-80% of pharmaceutical drugs in phase I metabolism in the liver.
Pharmaceutical companies involved in drug research and drug development actively study CYP pathways to determine the effect of new drugs on CYP metabolic activity.
CYP Subfamily Nomenclature
The CYP family is separated into subfamilies of proteins based on similar gene sequences. With regards to nomenclature, each family is first assigned a number (e.g., CYP1, CYP2), then a subfamily letter (e.g., CYP1A, CYP2B), and finally a number based on the enzyme isoform (e.g., CYP1A4, CYP2B3).CYP proteins in the same family should share greater than 40% amino acid similarity, while proteins in the same subfamily should share a greater than 55% similarity. In humans, there are fifty-seven known functional genes that code for CYPs2.
Cytochrome P450 in Drug Metabolism
CYPs are cited as the most important class of enzymes involved in drug metabolism and account for extreme variation of efficacy between patients. While drug metabolism can occur in many sites throughout the body the primary site is the liver.Foreign substance processing in the liver is vital for maintaining homeseotasis and is divided into two main types of metabolism. Phase I metabolism refers to the molecular changes made to foreign substances that induce hydrophilicity. These reactions are usually performed by CYPs and involve the addition or unmasking of a hydroxyl group on the foreign substance.
While phase I is usually sufficient to eliminate most compounds, more complex substances proceed through phase II metabolism to increase solubility. The addition of large polar groups in this phase is essential for ensuring that the compounds can be water-soluble and successfully eliminated by the kidneys3.
Complications in the CYP Pathway
One reason why CYPs are a key focus in R&D and clinical studies is the potential for CYP-mediated pathways to be influenced by the introduction of one or more new drugs. Drugs that act on these pathways may change the rate, efficiency, and ability of CYP proteins to properly metabolize all foreign substances. Therefore, drugs with similar metabolic pathways have the potential to induce negative effects on CYP metabolism.Six CYPs have been identified as key players in drug metabolism in humans:
- CYP1A2
- CYP2C19
- CYP2C9
- CYP2D6
- CYP2E1
- CYP3A4






.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)





.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)



.jpg)




.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)





